Organizational Structure for Companies With Examples and Benefits
Investopedia / Julie Bang
What Is an Organizational Structure?
An organizational structure is a system that outlines how certain activities are directed in order to achieve the goals of an organization. These activities can include rules, roles, and responsibilities.
The organizational structure also determines how information flows between levels within the company. For example, in a centralized structure, decisions flow from the top down, while in a decentralized structure, decision-making power is distributed among various levels of the organization. Having an organizational structure in place allows companies to remain efficient and focused.1
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- An organizational structure outlines how certain activities are directed to achieve the goals of an organization.
- Successful organizational structures define each employee's job and how it fits within the overall system.
- A centralized structure has a defined chain of command, while decentralized structures give almost every employee receiving a high level of personal agency.
- Types of organizational structures include functional, divisional, flatarchy, and matrix structures.
- Senior leaders should consider a variety of factors before deciding which type of organization is best for their business, including the business goals, industry, and culture of the company.
Understanding an Organizational Structure
Businesses of all shapes and sizes use organizational structures heavily. They define a specific hierarchy within an organization. A successful organizational structure defines each employee's job and how it fits within the overall system. Put simply, the organizational structure lays out who does what so the company can meet its objectives.
This structuring provides a company with a visual representation of how it is shaped and how it can best move forward in achieving its goals. Organizational structures are normally illustrated in some sort of chart or diagram like a pyramid, where the most powerful members of the organization sit at the top, while those with the least amount of power are at the bottom.
Organizational structure (OS) is the systematic arrangement of human resources in an organization so as to achieve common business objectives. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of every member of the organization so that work and information flow seamlessly, ensuring the smooth functioning of an organization.
An OS displays how different resources of an organization come together and align with its goals. It clearly defines the functions of employees that enable them to work harmoniously and efficiently. This reduces wastage of resources and increases productivity. The OS of a company establishes its workflow. Without a proper OS, there would be chaos in a business. Thus, a company must create a centralized or decentralized OS depending on its workflow needs.
Organizational Structure Explained
An organizational structure is the grouping of resources at different levels depending on their responsibilities, power, and position. It helps various departments in a company exchange data, coordinate, and work together to achieve business goals.
A company devises an organizational structure to ensure that suitable employees with the right set of skills occupy each position in the company. The OS reveals the accountability and authority of each role. This removes any uncertainty with regard to task performance and reporting and enhances employee productivity.
A company must clearly define its objectives before creating an OS. Then, group similar activities together to create departments, identify resources for each unit, and establish a hierarchy of employees based on their duties.
Thus, an OS of a company:
- Forms the basis of employee reporting and relations
- Decides the post of employees in their administrative divisions
- Formulates a system of coordination and interdependence in an organization
- Establishes a well-defined workflow aimed at attaining organizational goals
Every OS contains the following six essential elements:
- Work design: It defines the nature and job description of a particular position
- Administrative division: It involves the grouping of jobs into departments to facilitate the coordination of work.
- Deputation: It means the power conferred to each employee and department in the organization.
- Management ratio: It refers to the number of employees that are reporting to a supervisor.
- Hierarchy: It creates various levels of authority arranged in the order of delegated powers in the organization.
- Centralization or decentralization: It presents the mode of operation followed in an organization.
Not having a formal structure in place may prove difficult for certain organizations. For instance, employees may have difficulty knowing to whom they should report. That can lead to uncertainty as to who is responsible for what in the organization.
Having a structure in place can help with efficiency and provide clarity for everyone at every level. That also means each and every department can be more productive, as they are likely to be more focused on energy and time.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Organizational Structures
An organizational structure is either centralized or decentralized. Traditionally, organizations have been structured with centralized leadership and a defined chain of command. The military is an organization famous for its highly centralized structure, with a long and specific hierarchy of superiors and subordinates. In a centralized organizational system, there are very clear responsibilities for each role, with subordinate roles defaulting to the guidance of their superiors.
There has been a rise in decentralized organizations, as is the case with many technology startups. This allows companies to remain fast, agile, and adaptable, with almost every employee receiving a high level of personal agency. For example, Johnson & Johnson is a company that's known for its decentralized structure.2
As a large company with over 200 business units and brands that function in sometimes very different industries, each operates autonomously. Even in decentralized companies, there are still usually built-in hierarchies (such as the chief operating officer operating at a higher level than an entry-level associate). However, teams are empowered to make their own decisions and come to the best conclusion without necessarily getting "approval" from up top.
Types of Organizational Structures
Functional Structure
Four types of common organizational structures are implemented in the real world. The first and most common is a functional structure. This is also referred to as a bureaucratic organizational structure and breaks up a company based on the specialization of its workforce. Most small-to-medium-sized businesses implement a functional structure. Dividing the firm into departments consisting of marketing, sales, and operations is the act of using a bureaucratic organizational structure.
Divisional or Multidivisional Structure
The second type is common among large companies with many business units. Called the divisional or multidivisional (M-Form) structure, a company that uses this method structures its leadership team based on the products, projects, or subsidiaries they operate. A good example of this structure is Johnson & Johnson. With thousands of products and lines of business, the company structures itself so each business unit operates as its own company with its own president.
Divisions may also be designated geographically in addition to specialization. For instance, a global corporation may have a North American Division and a European Division.
Team-Based
Similar to divisional or functional structures, team-based organizations segregate into close-knit teams of employees that serve particular goals and functions, but where each team is a unit that contains both leaders and workers.
Flat (Flatarchy) Structure
Flatarchy, also known as a horizontal structure, is relatively newer, and is used among many startups. As the name alludes, it flattens the hierarchy and chain of command and gives its employees a lot of autonomy. Companies that use this type of structure have a high speed of implementation.
Matrix Structure
Firms can also have a matrix structure. It is also the most confusing and the least used. This structure matrixes employees across different superiors, divisions, or departments. An employee working for a matrixed company, for example, may have duties in both sales and customer service.
Circular Structure
Circular structures are hierarchical, but they are said to be circular as it places higher-level employees and managers at the center of the organization with concentric rings expanding outward, which contain lower-level employees and staff. This way of organizing is intended to encourage open communication and collaboration among the different ranks.
Network Structure
The network structure organizes contractors and third-party vendors to carry out certain key functions. It features a relatively small headquarters with geographically-dispersed satellite offices, along with key functions outsourced to other firms and consultants.
Benefits of Organizational Structures
Putting an organizational structure in place can be very beneficial to a company. The structure not only defines a company's hierarchy but also allows the firm to lay out the pay structure for its employees. By putting the organizational structure in place, the firm can decide salary grades and ranges for each position.
The structure also makes operations more efficient and much more effective. By separating employees and functions into different departments, the company can perform different operations at once seamlessly.
In addition, a very clear organizational structure informs employees on how best to get their jobs done. For example, in a hierarchical organization, employees will have to work harder at buying favor or courting those with decision-making power. In a decentralized organization, employees must take on more initiative and bring creative problem solving to the table. This can also help set expectations for how employees can track their own growth within a company and emphasize a certain set of skills—as well as for potential employees to gauge if such a company would be a good fit with their own interests and work styles.
What Are Some Types of Organizational Structures?
The four types of organizational structures are functional, multi-divisional, flat, and matrix structures. Others include circular, team-based, and network structures.
What Are the Key Elements of an Organizational Structure?
Key elements of an organizational structure include how certain activities are directed in order to achieve the goals of an organization, such as rules, roles, responsibilities, and how information flows between levels within the company.
What Is an Organizational Structure Example?
An example of an organizational structure is a decentralized structure, which gives individuals and teams high degrees of autonomy without needing a core team to regularly approve business decisions. A good example of this decentralized structure is Johnson & Johnson. With thousands of products and lines of business, the company structures itself so each business unit operates as its own company with its own president.
What Is an Organizational Structure Chart?
Organizational structures are normally illustrated in some sort of chart or diagram like a pyramid, where the most powerful members of the organization sit at the top, while those with the least amount of power are at the bottom.
What Is the Best Organizational Structure?
There is no one best organizational structure, as it depends on the nature of the company and the industry it operates in.
The Bottom Line
There are entire fields of study based on how to optimize and best structure organizations to be the most effective and productive. Senior leaders should consider a variety of factors before deciding which type of organization is best for their business, including the business goals, industry, and culture of the company.
Centralization or Centralized Organizational Structure
In this system, all the powers of decision-making rest at the topmost level of the management. They take the shape of a pyramid with the leader or executive team at the top responsible for making all decisions. Below them are departmental managers overseeing supervisors. These supervisors lead the workers at the lowest level in the hierarchy.
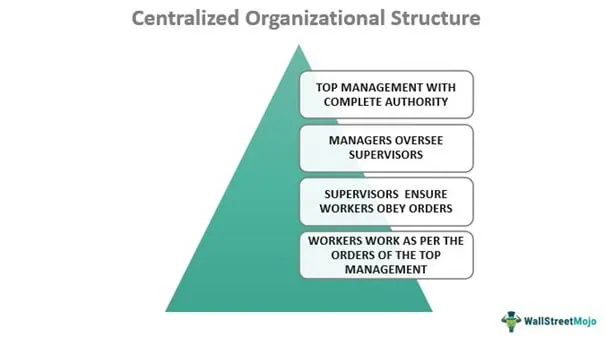
You are free to use this image on your website, templaes, etc, Please provide us with an attribution link
A centralized OS structure gives uniformity of policy when the operational units face a conflict of objectives and strategic goals. Also, it speeds up the decision-making process. This type of OS is prevalent in the retail industry.
Decentralization or Decentralized Organizational Structure
In this system of OS, an organization’s middle- and lower-level managers make decisions as per the local culture or laws. This leaves the top management to direct its attention to major decisions. This type of OS flattens the hierarchy and empowers employees. It is widely prevalent in the hotel sector.
The hotel sector has to comply with local laws to function properly in areas of food and beverages, human resources (HR), and operations. Therefore, decentralization is required because handling the guests, food, staff, and processes with a centralized structure is impossible.
Types of Organizational Structure
Organizations implement different types of OS depending on the nature of their business, needs of customers, types of products in demand, and services required. Here are some of the popular organizational structures.
#1 – Hierarchical
This is a type of centralized organizational structure. There is a hierarchy of workers with leaders at the top, the workers below, and supervisors placed in between to get the work done. It is more of a linear OS where the delegation of power emanates from the top management. It is a widely popular form of OS and is seen in companies like Amazon.
This system concentrates decision-making at the top level. As a result, the organization suffers from a lack of creativity as innovative ideas have to work their way up through various levels of management. Also, each employee communicates with their immediate superior and subordinates only. This reduces coordination at various levels of power and departments. Nevertheless, it is a salient feature of most government organizations.
#2 – Flat
This organizational structure is devoid of any hierarchy. No one commands or controls the employees. Instead, decisions are made at every level of management. Therefore, it is usually used in small companies with few employees or new startups. However, with time and business growth, some form of hierarchy creeps into the organization; otherwise, it may cause chaos and inefficiency in the organization.
#3 – Flatarchy
It includes features of both hierarchical and flat OS. It is a temporary form of OS that comes into existence only when a new product is created, a new service is being tested, or when a company seeks to develop a new customer support system.
By employing flatarchy, an organization can have specialized teams to handle the development of new products or services more creatively and efficiently. It is the best tool for an organization to tackle the change in market or industry sentiments without creating capital-intensive departments or reforming the OS.
#4 – Functional
The functional organizational structure creates a fixed set of departments based on certain functions like HR, accounts, marketing, etc. It segregates the workforce based on the requirements of each department. For example, an accounting departmentwill employ accountants and work to manage the firm’s finances in the best possible manner.
Likewise, the HR department will look after the recruitment, payroll, and administration of the firm. Moreover, the functional OS allows the employees to work for a particular functional role without worrying about the other departments. So, for example, a sales executive won’t be worried about a firm’s accounting work and vice versa.
#5 – Divisional
This type of organizational structure comes into play when a firm has grown exponentially to become a giant in its sector. For example, a giant clothing company will require separate divisions based on customer groups, product types, and geographical locations.
Hence, it will create a ladies’ fashion garment division, kids wear division, men’s wear division, and affordable clothing division. Each division will have its own production, marketing, human resource, IT, and sales teams. In this manner, the company could manage the product line or geography with all necessary functional resources.
#6 – Matrix
Under this organizational structure, there is no clear demarcation of roles and responsibilities of resources. Resources may be shared across different teams to ensure their maximum utilization. It is the least used OS as it is quite complex and confusing and may prove counter-productive.
The employees have to play a dual role in this OS. For example, the customer service representative in many banks also acts as their cashier. It may reduce operating costs but badly affects the employee’s quality of work and the firm’s efficiency. It is a form of decentralized OS.
Examples
Let’s take the help of organizational structure examples to understand the working of the OS more comprehensively.
Example #1
Here is an example from the healthcare sector, which utilizes the organizational structure for meeting its business, customer care, employee relations, and healthcare objectives. Suppose a multi-specialty hospital, Life-medical Healthcare Ltd, provides 247365 services to the patients, including surgery, emergency services, and outdoor patient services.
Therefore, it creates an OS chart for the best services and healthcare to cater to their patient’s needs. The OS segregates the hospital into functional departments. Specialized staff is appointed under each department based on its requirements. The roles, responsibilities, and reporting of each employee are fixed. The OS chart would appear as follows:
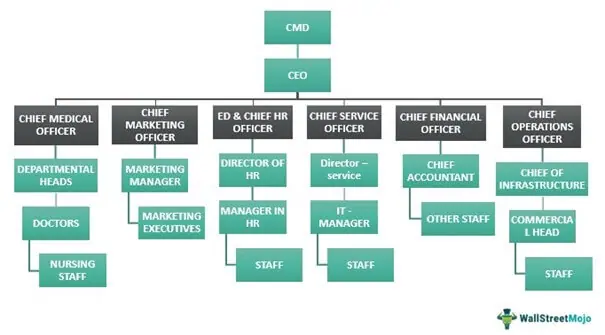
You are free to use this image on your website, templaes, etc, Please provide us with an attribution link
Examples #2
Let us assume a coffee shop Sipping Paradise has its operations expanded to western, northern, eastern, and southern parts of Japan. Therefore, it creates a divisional OS wherein its business operation is segregated based on the geographical locations of the business.
The Sipping Paradise divides its operational areas into the western, northern, eastern, and southern divisions to monitor and control the business properly. Each division has separate accounts and finance, human resources, marketing, and operations departments. Each division makes its own operational decisions.
Such an OS will enable the company to offer localized services and quickly respond to customer needs of a specific location. However, it may lead to duplication of resources and higher costs for the company.
Benefits
An ideal OS helps in the efficient operation of a company. Some of the benefits of OS are as follows.
- Swift decision-making possible – The organizational structure helps the flow of information effortlessly across different levels of management. It enables quick decision-making.
- Coordination between different geographical divisions of a company – OS promotes easy administration and working of an organization at multiple locations. A well-defined OS enables better coordination between different units at various locations to ensure the attainment of common organizational goals.
- Enhances efficiency and productivity – OS improves the level of efficiency as the staff knows their roles and responsibilities, and the supervisor knows what to expect of their subordinates. Thus, it improves productivity in general.
- Empowers employees – When workers have specific roles and duties according to their skill set, they learn and become competent. Thus, OS boosts their confidence and empowers them.
- Reduces conflict within an organization – If an employee knows the scope of his work, there is no possibility of conflict with other workers. Thus, OS reduces friction among the workers.
- Better communication among members – OS establishes excellent communication between the management, supervisors, and workers. This promotes an effective flow of information and work.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Organizational Structure is important for every business because it helps bring out a homogeneity of function and administration across the organization. It assists in handling the workforce efficiently and enables better coordination between various divisions. Moreover, an organized structure helps deal with customer needs and enhances the firm’s revenues.
The different types of organizational structures (OS) are hierarchical, functional, divisional, flatarchy, and matrix. The most common OS in use in all the companies is the functional OS. This model puts the workforce into various groups and divisions depending on their job role and functions as the HR department, accounts department, marketing department, etc.
The healthcare sector has to address the needs of patients with different conditions that specialist doctors can address. Therefore, the healthcare sector utilizes the functional organizational structure to group the patients with similar nature of illnesses into one group. After that, these groups of patients are assigned to autonomous departments that set the appropriate doctors for these patients. Thus, the patients, doctors, and the departments coordinate efficiently under the functional OS.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/organizationalstructure-final-5d4f333cdb174faea796402175ff305b.png)



टिप्पणियाँ
एक टिप्पणी भेजें